RabbitMQ topic example with symfony including 1 Producer & 1 Exchange & 2 Queue & N Worker & 2 Consumer
20/02/2016 - RABBITMQ, SYMFONY
In this example we're going to create a new purchase order for "bmw", "audi", "mercedes" and take logs of it. Orders will be coming from a single producer. It consists of 1 Producer & 1 Exchange & 2 Queue & N Worker & 2 Consumer. In such scenario, "bmw" orders get treated differently compared to "audi" and "mercedes" orders which get treated in same way. Example uses RabbitMqBundle.
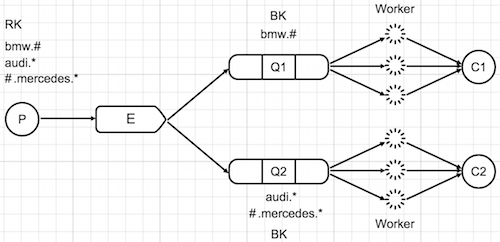
How it works
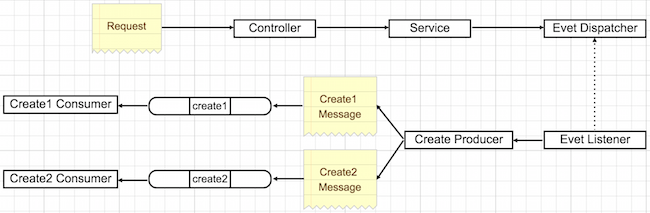
- Request - User places an order create request.
- Controller - Request gets validated and passed on to Service.
- Service - A new order gets inserted into database, an order create event is created and the response is returned to user. This is where application process is finished so no more waiting time for user.
- Event Dispatcher - Picks up the event and dispatches it.
- Event Listener - Picks up dispatched event and passes it on to Producer.
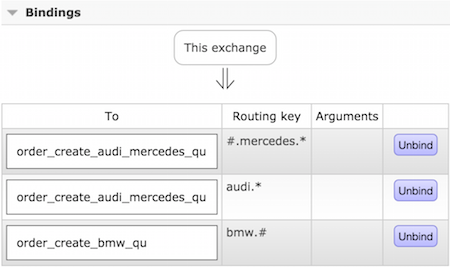
- Producer - Creates a message and puts it into either in "bwm" or "audi_mercedes" queue.
- Consumer - If the worker is running in terminal, it catches the message and processes it. If the worker is not running yet, it would start consuming messages later on when the worker is started.
Configurations
Install bundle
Install "oldsound/rabbitmq-bundle":"1.8.0" with composer and activate it with new OldSound\RabbitMqBundle\OldSoundRabbitMqBundle() in AppKernel.php file.
Parameters.yml
parameters:
rabbit_mq_host: 127.0.0.1
rabbit_mq_port: 5672
rabbit_mq_user: guest
rabbit_mq_pswd: guest
Config.yml
old_sound_rabbit_mq:
connections:
default:
host: %rabbitmq.host%
port: %rabbitmq.port%
user: %rabbitmq.user%
password: %rabbitmq.pswd%
vhost: /
lazy: true
producers:
order_create:
connection: default
exchange_options: { name: order_create_ex, type: topic }
consumers:
order_create_bmw:
connection: default
exchange_options: { name: order_create_ex, type: topic }
queue_options:
name: order_create_bmw_qu
routing_keys:
- 'bmw.#'
callback: application_frontend.consumer.order_create_bmw
order_create_audi_mercedes:
connection: default
exchange_options: { name: order_create_ex, type: topic }
queue_options:
name: order_create_audi_mercedes_qu
routing_keys:
- 'audi.*'
- '#.mercedes.*'
callback: application_frontend.consumer.order_create_audi_mercedes
OrderController
You should normally validate the request and map it into a model class. There are a lot of examples about how it is done in this blog.
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Controller;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Service\OrderService;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Route;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Method;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
/**
* @Route("order", service="application_frontend.controller.order")
*/
class OrderController
{
private $orderService;
public function __construct(OrderService $orderService)
{
$this->orderService = $orderService;
}
/**
* @param Request $request
*
* @Method({"POST"})
* @Route("/create")
*
* @return Response
*/
public function createAction(Request $request)
{
$result = $this->orderService->create(json_decode($request->getContent(), true));
return new Response($result);
}
}
Controllers.yml
services:
application_frontend.controller.order:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\Controller\OrderController
arguments:
- @application_frontend.service.order
OrderService
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Service;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Entity\Order;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Event\OrderEvent;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventDispatcherInterface;
class OrderService
{
private $entityManager;
private $eventDispatcher;
public function __construct(
EntityManagerInterface $entityManager,
EventDispatcherInterface $eventDispatcher
) {
$this->entityManager = $entityManager;
$this->eventDispatcher = $eventDispatcher;
}
/**
* @param array $newOrder
*
* @return Order
*/
public function create(array $newOrder)
{
$order = new Order();
$order->setCustomerName($newOrder['customer_name']);
$order->setCarMake($newOrder['car_make']);
$order->setCarModel($newOrder['car_model']);
$this->entityManager->persist($order);
$this->entityManager->flush();
$this->eventDispatcher->dispatch(OrderEvent::CREATE, new OrderEvent($order));
return $order->getId();
}
}
Services.yml
services:
application_frontend.service.order:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\Service\OrderService
arguments:
- @doctrine.orm.entity_manager
- @event_dispatcher
OrderEvent
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Event;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Entity\Order;
use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\Event;
class OrderEvent extends Event
{
const CREATE = 'application_frontend.event.order_create';
private $order;
public function __construct(Order $order)
{
$this->order = $order;
}
public function getOrder()
{
return $this->order;
}
}
OrderListener
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\EventListener;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Event\OrderEvent;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Producer\OrderCreateProducer;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Log\LoggerInterface;
class OrderListener
{
private $orderCreateProducer;
public function __construct(OrderCreateProducer $orderCreateProducer)
{
$this->orderCreateProducer = $orderCreateProducer;
}
public function onOrderCreate(OrderEvent $orderEvent)
{
$this->orderCreateProducer->add($orderEvent->getOrder());
$orderEvent->stopPropagation();
}
}
Listeners.yml
services:
application_frontend.event_listener.order:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\EventListener\OrderListener
tags:
- { name: kernel.event_listener, event: application_frontend.event.order_create, method: onOrderCreate }
arguments:
- @application_frontend.producer.order_create
OrderCreateProducer
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Producer;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Entity\Order;
use OldSound\RabbitMqBundle\RabbitMq\ProducerInterface;
class OrderCreateProducer
{
private $producer;
public function __construct(ProducerInterface $producer)
{
$this->producer = $producer;
}
public function add(Order $order)
{
$message = [
'order_id' => $order->getId(),
'customer_name' => $order->getCustomerName(),
'car_make' => $order->getCarMake(),
'car_model' => $order->getCarModel(),
'timestamp' => date('Y-m-d H:i:s')
];
$this->producer->publish(json_encode($message), $message['car_make']);
}
}
Producers.yml
services:
application_frontend.producer.order_create:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\Producer\OrderCreateProducer
arguments:
- @old_sound_rabbit_mq.order_create_producer
OrderCreateBmwConsumer
There is a reason why we just log failed messages and do nothing about them. You can find the post related to the answer in this blog.
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Consumer;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Entity\OrderLog;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Exception;
use OldSound\RabbitMqBundle\RabbitMq\ConsumerInterface;
use PhpAmqpLib\Message\AMQPMessage;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Log\LoggerInterface;
class OrderCreateBmwConsumer implements ConsumerInterface
{
private $entityManager;
private $logger;
public function __construct(
EntityManagerInterface $entityManager,
LoggerInterface $logger
) {
$this->entityManager = $entityManager;
$this->logger = $logger;
}
public function execute(AMQPMessage $message)
{
$body = json_decode($message->body, true);
try {
$this->log($body);
echo sprintf('Order create - ID:%s @ %s ...', $body['order_id'], date('Y-m-d H:i:s')).PHP_EOL;
echo json_encode($message).PHP_EOL;
} catch (Exception $e) {
$this->logError($message, $e->getMessage());
}
}
private function log($message)
{
$log = new OrderLog();
$log->setAction(OrderLog::CREATE.' '.$message['car_make']);
$log->setMessage($message);
$this->entityManager->persist($log);
$this->entityManager->flush();
}
private function logError($message, $error)
{
$data = [
'error' => $error,
'class' => __CLASS__,
'message' => $message
];
$this->logger->error(json_encode($data));
}
}
OrderCreateAudiMercedesConsumer
There is a reason why we just log failed messages and do nothing about them. You can find the post related to the answer in this blog.
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Consumer;
use Application\FrontendBundle\Entity\OrderLog;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Exception;
use OldSound\RabbitMqBundle\RabbitMq\ConsumerInterface;
use PhpAmqpLib\Message\AMQPMessage;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Log\LoggerInterface;
class OrderCreateAudiMercedesConsumer implements ConsumerInterface
{
private $entityManager;
private $logger;
public function __construct(
EntityManagerInterface $entityManager,
LoggerInterface $logger
) {
$this->entityManager = $entityManager;
$this->logger = $logger;
}
public function execute(AMQPMessage $message)
{
$body = json_decode($message->body, true);
try {
$this->log($body);
echo sprintf('Order create - ID:%s @ %s ...', $body['order_id'], date('Y-m-d H:i:s')).PHP_EOL;
echo json_encode($message).PHP_EOL;
} catch (Exception $e) {
$this->logError($message, $e->getMessage());
}
}
private function log($message)
{
$log = new OrderLog();
$log->setAction(OrderLog::CREATE.' '.$message['car_make']);
$log->setMessage($message);
$this->entityManager->persist($log);
$this->entityManager->flush();
}
private function logError($message, $error)
{
$data = [
'error' => $error,
'class' => __CLASS__,
'message' => $message
];
$this->logger->error(json_encode($data));
}
}
If the message processing fails for some reason, log would have record below.
# app/log/dev.log
[2016-01-31 22:32:10] app.ERROR: {"error":"Catchable Fatal Error: Object of class PhpAmqpLib\\Message\\AMQPMessage could not be converted to string","class":"Application\\FrontendBundle\\Consumer\\OrderCreateBmwConsumer","message":{"body":"{\"order_id\":39,\"customer_name\":\"inanzzz\",\"car_make\":\"bmw\",\"car_model\":\"318\",\"timestamp\":\"2016-02-02 22:32:09\"}","body_size":"110","is_truncated":false,"content_encoding":null,"delivery_info":{"channel":{"callbacks":{"PHPPROCESS-MacBook-Pro.local_93134":[{},"processMessage"]}},"consumer_tag":"PHPPROCESS-MacBook-Pro.local_93134","delivery_tag":"1","redelivered":false,"exchange":"order_create_ex","routing_key":"bmw"}}} [] []
# Terminal
[2016-01-31 22:32:10] app.ERROR: {"error":"Catchable Fatal Error: Object of class PhpAmqpLib\\Message\\AMQPMessage could not be converted to string","class":"Application\\FrontendBundle\\Consumer\\OrderCreateBmwConsumer","message":{"body":"{\"order_id\":39,\"customer_name\":\"inanzzz\",\"car_make\":\"bmw\",\"car_model\":\"318\",\"timestamp\":\"2016-02-02 22:32:09\"}","body_size":"110","is_truncated":false,"content_encoding":null,"delivery_info":{"channel":{"callbacks":{"PHPPROCESS-MacBook-Pro.local_93134":[{},"processMessage"]}},"consumer_tag":"PHPPROCESS-MacBook-Pro.local_93134","delivery_tag":"1","redelivered":false,"exchange":"order_create_ex","routing_key":"bmw"}}}
Consumers.yml
services:
application_frontend.consumer.order_create_bmw:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\Consumer\OrderCreateBmwConsumer
arguments:
- @doctrine.orm.entity_manager
- @logger
application_frontend.consumer.order_create_audi_mercedes:
class: Application\FrontendBundle\Consumer\OrderCreateAudiMercedesConsumer
arguments:
- @doctrine.orm.entity_manager
- @logger
Order entity
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* @ORM\Entity
* @ORM\Table(name="orders")
*/
class Order
{
/**
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\Column(type="smallint")
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
private $id;
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="customer_name", type="string", length=50)
*/
private $customerName;
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="car_make", type="string", length=50)
*/
private $carMake;
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="car_model", type="string", length=50)
*/
private $carModel;
}
OrderLog entity
namespace Application\FrontendBundle\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* @ORM\Entity
* @ORM\Table(name="order_log")
*/
class OrderLog
{
const CREATE = 'Create';
/**
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\Column(type="smallint")
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
private $id;
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="action", type="string", length=50)
*/
private $action;
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="message", type="json_array")
*/
private $message;
}
Tests
These are the kind of payloads we're going to use for testing purposes when creating new orders.
# POST http://rabbitmq.dev/app_dev.php/order/create
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "bmw",
"car_model": "318"
}
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "bmw.three",
"car_model": "318"
}
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "audi.a",
"car_model": "a3"
}
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "mercedes.benz",
"car_model": "sl500"
}
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "amg.mercedes.benz",
"car_model": "sl500"
}
{
"customer_name": "inanzzz",
"car_make": "mc.laren.mercedes.benz",
"car_model": "sl500"
}
Run a consumers and stop them so that you have the RabbitMQ components (exchange, queue etc.) are ready and bound together otherwise messages will be lost. You should have a visualised diagram below.
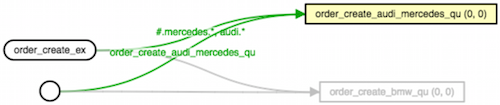

Test 1: No consumer running
I created 6 new orders.
mysql> SELECT * FROM orders;
+----+---------------+------------------------+-----------+
| id | customer_name | car_make | car_model |
+----+---------------+------------------------+-----------+
| 1 | inanzzz | bmw | 318 |
| 2 | inanzzz | bmw.three | 318 |
| 3 | inanzzz | audi.a | a3 |
| 4 | inanzzz | mercedes.benz | sl500 |
| 5 | inanzzz | amg.mercedes.benz | sl500 |
| 6 | inanzzz | mc.laren.mercedes.benz | sl500 |
+----+---------------+------------------------+-----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM order_log;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
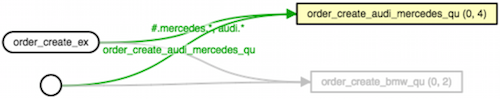
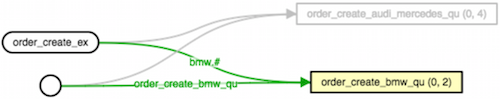
As you can see above, there are 2 messages waiting in "bmw" queue and 4 messages in "audi_mercedes" queue. I'm now going to run a consumer to show what happens. You might need to close dead connections otherwise messages won't be redelivered.
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_bmw
Order create - ID:1 @ 2016-02-20 20:34:01 ...
Order create - ID:2 @ 2016-02-20 20:34:22 ...
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_audi_mercedes
Order create - ID:3 @ 2016-02-20 20:34:34 ...
Order create - ID:4 @ 2016-02-20 20:34:50 ...
Order create - ID:5 @ 2016-02-20 20:35:01 ...
Order create - ID:6 @ 2016-02-20 20:35:08 ...
mysql> SELECT * FROM order_log;
+----+-------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | action | message |
+----+-------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | Create bmw | {"order_id":1,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"bmw","car_model":"318","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:34:01"} |
| 2 | Create bmw.three | {"order_id":2,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"bmw.three","car_model":"318","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:34:22"} |
| 3 | Create audi.a | {"order_id":3,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"audi.a","car_model":"a3","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:34:34"} |
| 4 | Create mercedes.benz | {"order_id":4,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"mercedes.benz","car_model":"sl500","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:34:50"} |
| 5 | Create amg.mercedes.benz | {"order_id":5,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"amg.mercedes.benz","car_model":"sl500","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:35:01"} |
| 6 | Create mc.laren.mercedes.benz | {"order_id":6,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"mc.laren.mercedes.benz","car_model":"sl500","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:35:08"} |
+----+-------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)


As you can see above, all pending messages have been consumed.
Test 2: Two consumer running for each create consumers
I created 3 new "bmw" and 2 "audi/mercedes" orders.
mysql> SELECT * FROM orders;
+----+---------------+---------------+-----------+
| id | customer_name | car_make | car_model |
+----+---------------+---------------+-----------+
| 1 | inanzzz | bmw | 318 |
| 2 | inanzzz | bmw.five | 5.20 |
| 3 | inanzzz | bmw.m | m3 |
| 4 | inanzzz | audi.a | a3 |
| 5 | inanzzz | mercedes.benz | sl500 |
+----+---------------+---------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM order_log;
+----+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | action | message |
+----+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | Create bmw | {"order_id":1,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"bmw","car_model":"318","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:48:10"} |
| 2 | Create bmw.five | {"order_id":2,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"bmw.five","car_model":"5.20","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:48:35"} |
| 3 | Create bmw.m | {"order_id":3,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"bmw.m","car_model":"m3","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:48:44"} |
| 4 | Create audi.a | {"order_id":4,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"audi.a","car_model":"a3","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:49:11"} |
| 5 | Create mercedes.benz | {"order_id":5,"customer_name":"inanzzz","car_make":"mercedes.benz","car_model":"sl500","timestamp":"2016-02-20 20:49:18"} |
+----+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)

# Create bmw Consumer 1
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_bmw
Order create - ID:1 @ 2016-02-20 20:48:10 ...
Order create - ID:3 @ 2016-02-20 20:48:44 ...
# Create bmw Consumer 2
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_bmw
Order create - ID:2 @ 2016-02-20 20:48:35 ...
# Create audi/mercedes Consumer 1
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_audi_mercedes
Order create - ID:4 @ 2016-02-20 20:49:11 ...
# Create audi/mercedes Consumer 2
$ app/console rabbitmq:consumer -m 100 order_create_audi_mercedes
Order create - ID:5 @ 2016-02-20 20:49:18 ...
As you can see above, all 5 create messages have been consumed right away by four consumers in round-robin dispatching way.
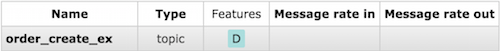
RabbitMQ Management
Exchange
Queue
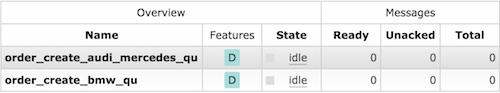
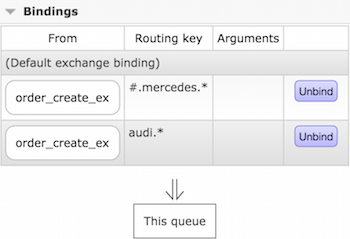

Mapping

