İstekleri Nginx reverse proxy ile ilgili sunuculara yönlendirme ve istemcinin istek başlıklarını günlüğe kaydetme
31/03/2019 - DOCKER, LINUX, SYMFONY, NGINX
Bu örnekte, kullanıcıdan gelen istekleri ilgili uygulama sunucularına iletmek için Nginx'in Reverse Proxy özelliğini kullanacağız. İstek URL'sini kontrol edeceğiz ve isteği iletmek için alakalı uygulamayı seçeceğiz. Bu yaklaşım genelde, iç ağınızı İnternete maruz bırakmak istemiyorsanız kullanılır. Çözüm, tek bir sunucunun sizin için trafiği yönetmesine izin vermek. Örneğimiz Docker containerler üzerine kurulu ve tüm containerler bir Linux makinesinde çalışıyor. Daha fazla bilgi için Nginx Reverse Proxy sayfasını okuyabilirsiniz.
Çalışma mantığı
Ağımızda 3 özel uygulama sunucumuz (Authentication, Restful ve Website) ve 1 tanede Internet'e açık Nginx reverse proxy sunucumuz (Gateway) var.
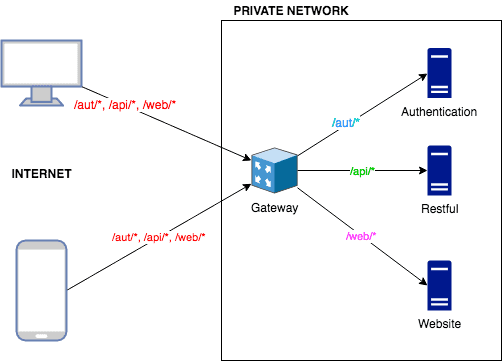
Yukarıda görebileceğiniz gibi, tüm istekler "Gateway" nginx sunucusuna gidiyor ve ardından isteğin URL'sine bakılarak trafiğin nereye yönlendirileceğine karar veriliyor.
/aut/*için gelen istekler "authentication" uygulama sunucusuna yönlendiriliyor./api/*için gelen istekler "restful" uygulama sunucusuna yönlendiriliyor./web/*için gelen istekler "website" uygulama sunucusuna yönlendiriliyor.
URL'si uygunsuz olan diğer istekler ise "404 Bad Request" cevabı alıyorlar.
Notlar
- Gateway sunucusu İnternet erişimine açık olmalı ve HTTP değil HTTPS kullanmalıdır - Sadece gösteri amaçlı olarak HTTP'yi de ekledim.
- İnternetten, diğer tüm özel sunuculara doğrudan erişim engellenmelidir. Gereksinimlere bağlı olarak, hem HTTP hem de HTTPS etkinleştirilebilir. Şu anda Gateway sunucusu tüm istekleri yalnızca tanıtım amacıyla HTTP'ye yönlendirir.
- Tüm özel sunucular, kendi request ID bilgileriyle birlikte Gateway sunucusunun request ID bilgisinide log içinde kaydederler.
- Gerçek istemci ve proxy sunucusu ile ilgili bilgiler özel sunuculara iletilir ve global
$_SERVERdeğişkenindeHTTP_X_****kafası ve sunucu ortam değişkeni olarak kullanılabilir halde olurlar. Aşağıdaki "İsteğe Bağlı" Symfony örneğine bakın. - Bu örnek Docker container kullanır ve tüm Nginx sunucu günlükleri
stdout'a gönderilir. Eğer isterseniz$ docker logs -f {nginx_container_name}komutu ile günlükleri okuyabilirsiniz. - Daha iyi okunabilirlik sağlamak için Nginx günlükleri JSON formatında uygulama containerlarına yazılırlar.
Gereksinimler
- Gateway sunucusunun request ID bilgisi uygulama sunucularına iletilir ve böylece hem Gateway hem de uygulama sunucusunun request ID bilgisi günlük dosyalarında bulunurlar. Bu bize, bir kişinin isteğini ve uçtan uca yolculuğunu izlememize yardımcı olur. Not: Gateway'dan istek geldiğinde, eğer o isteği diğer bir uygulama sunucusuna iletiyorsanız,
x-request-trace-idkafa bilgisini isteğe eklemeyi unutmayın yoksa isteğin uçtan uca yolculuğunu kaybederiz. - Gateway sunucusunun request ID bilgisi asıl istemciye cevap kafası olarak iletilir. Bu aynı zamanda müşterinin isteğiyle ilişkili günlükleri bulmamıza yardımcı olur, aksi halde hangi istek kaydının hangi kullanıcının isteğine ait olduğunu bilemeyiz.
İsteğe Bağlı
Symfony uygulamanızda Nginx'ten gelen herhangi bir özel başlık verisini kaydetmek istiyorsanız, aşağıdakileri yapabilirsiniz.
# service.yaml
parameters:
env(HTTP_X_REQUEST_ID): ~
env(HTTP_X_REQUEST_TRACE_ID): ~
services:
App\Logger\XRequestIdProcessor:
arguments:
$xRequestId: '%env(string:HTTP_X_REQUEST_ID)%'
$xRequestTraceId: '%env(string:HTTP_X_REQUEST_TRACE_ID)%'
tags:
- { name: monolog.processor }
# Custom logger
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Logger;
class XRequestIdProcessor
{
private $xRequestId;
private $xRequestTraceId;
public function __construct(?string $xRequestId, ?string $xRequestTraceId)
{
$this->xRequestId = $xRequestId;
$this->xRequestTraceId = $xRequestTraceId;
}
public function __invoke(array $record)
{
$record['context']['x_request_id'] = $this->xRequestId;
$record['context']['x_request_trace_id'] = $this->xRequestTraceId;
return $record;
}
}
# The log
[06-Apr-2019 08:05:28] WARNING: [pool www] child 9 said into stdout: "[2019-04-06 08:05:28] request.INFO: Matched route "index". {"route":"index","route_parameters":{"_route":"index","_controller":"App\\Controller\\DockerController::index"},"request_uri":"http://192.168.99.30/","method":"GET","x_request_id":"bce165ceae2ff2b3d58999b834416301","x_request_trace_id":"c83354e6b40bc1ac1959e642bf892562"} []"
Ayrıca controller, event listener vs. gibi yerlerde $request->headers->get('x-request-*****') metodunu da kullanabilirsiniz.
Docker
İnternet'e kapalı olan özel sunucular "docker compose" kullanıyorlar çünkü hepsinde Nginx ve PHP-FPM çalışıyor. Fakat, İnternet'e açık olan Nginx proxy server sadece Nginx container kullanıyor bu nedenle "Dockerfile" yeterlidir.
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE PORTS NAMES
afbbfdc798e3 dev_aut_nginx 0.0.0.0:5080->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5443->443/tcp dev_aut_nginx_1
32cf3c89ef00 dev_aut_php 9000/tcp dev_aut_php_1
eb570837b30b dev_res_nginx 0.0.0.0:6080->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:6443->443/tcp dev_res_nginx_1
5c9d060723fd dev_res_php 9000/tcp dev_res_php_1
997a1906f891 dev_web_nginx 0.0.0.0:7080->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:7443->443/tcp dev_web_nginx_1
963af53f8c0c dev_web_php 9000/tcp dev_web_php_1
df86e2c2605d gateway:nginx 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8443->443/tcp gateway_1
Gateway nginx reverse proxy server oluşturmak ve çalıştırmak için aşağıdaki komutları kullandık.
$ docker build -t gateway:nginx .
$ docker run --name gateway_1 -p 8080:80 -p 8443:443 -d gateway:nginx
Tüm bu sunucuları doğrudan ana işletim sisteminden test etmek istiyorsanız, aşağıdaki komutları kullanabilirsiniz.
# AUTHENTICATION
curl -i http://localhost:5080
curl --insecure -i https://localhost:5443
# RESTFUL
curl -i http://localhost:6080
curl --insecure -i https://localhost:6443
# WEBSITE
curl -i http://localhost:7080
curl --insecure -i https://localhost:7443
# GATEWAY
curl -i http://localhost:8080
curl --insecure -i https://localhost:8443
Ana işletim sistemi olan Debian OS sunucusunun IP adresi 192.168.99.30 olarak geçiyor. Aşağıda da gördüğümüz gibi özel sunuculara ulaşımı bu IP adresini kullanarak Gateway reverse proxy server üzerinden test edebilirsiniz.
http://192.168.99.30:8080/{aut|api|web}/*
https://192.168.99.30:8443/{aut|api|web}/*
Dosyalar
Gateway
Dockerfile
FROM nginx:1.15.8-alpine
RUN apk add --no-cache bash
RUN rm -rf /var/cache/apk/*
COPY app.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY app_ssl.crt /etc/ssl/certs/app_ssl.crt
COPY app_ssl.key /etc/ssl/private/app_ssl.key
app.conf
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 default_server ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/app_ssl.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/app_ssl.key;
# Send traceable request id to client
add_header X-Request-Trace-ID $request_id;
# Pass traceable request id to upstream server
proxy_set_header X-Request-Trace-ID $request_id;
# Proxy server's host name/IP
proxy_set_header Host $host;
# Upstream server's schema
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Upstream server's host name(:port)/IP(:port)
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $proxy_host;
# Upstream server's port
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $proxy_port;
# Client's IP
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
# Any request URI starts with "/aut/*" gets forwarded to "authentication" application
location ~ ^/aut/(.*) {
proxy_pass http://172.17.0.1:5080/$1$is_args$args;
# proxy_pass https://172.17.0.1:5443/$1$is_args$args;
}
# Any request URI starts with "/api/*" gets forwarded to "restful" application
location ~ ^/api/(.*) {
proxy_pass http://172.17.0.1:6080/$1$is_args$args;
# proxy_pass https://172.17.0.1:6443/$1$is_args$args;
}
# Any request URI starts with "/web/*" gets forwarded to "website" application
location ~ ^/web/(.*) {
proxy_pass http://172.17.0.1:7080/$1$is_args$args;
# proxy_pass https://172.17.0.1:7443/$1$is_args$args;
}
# Return 404 for every other request URIs
location / {
return 404;
}
}
nginx.conf
user nginx;
# 1 worker process per CPU core.
# Check max: $ grep processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
# Tells worker processes how many people can be served simultaneously.
# worker_process (2) * worker_connections (2048) = 4096
# Check max: $ ulimit -n
worker_connections 2048;
# Connection processing method. The epoll is efficient method used on Linux 2.6+
use epoll;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format json_combined escape=json
'{'
'"time_local":"$time_local",'
'"client_ip":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"remote_addr":"$remote_addr",'
'"remote_user":"$remote_user",'
'"request":"$request",'
'"status": "$status",'
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",'
'"request_time":"$request_time",'
'"http_referrer":"$http_referer",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",'
'"request_id":"$request_id"'
'}';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log json_combined;
# Used to reduce 502 and 504 HTTP errors.
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
# The sendfile allows transfer data from a file descriptor to another directly in kernel.
# Combination of sendfile and tcp_nopush ensures that the packets are full before being sent to the client.
# This reduces network overhead and speeds the way files are sent.
# The tcp_nodelay forces the socket to send the data.
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
# The client connection can stay open on the server up to given seconds.
keepalive_timeout 65;
# Hides Nginx server version in headers.
server_tokens off;
# Sets the maximum size of the types hash tables.
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# Compress files on the fly before transmitting.
# Compressed files are then decompressed by the browsers that support it.
gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
Authentication
Diğer iki uygulama sunucusunun dosyaları aynı olduğundan bunları eklemeyeceğim. Malumdur ki, docker ile ilgili olan dosyalarda ufak farklılıklar olabilir. Mesela (aut, api, web) ve kullanılar portları gibi. Bununla birlikte PHP-FPM dosyalarını eklemeyeceğim çünkü onlar örneğimizle ilgili değiller.
docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
aut_php:
build:
context: "./php"
hostname: "aut-php"
volumes:
- "../..:/app:consistent"
environment:
PS1: "\\u@\\h:\\w\\$$ "
aut_nginx:
build:
context: "./nginx"
hostname: "aut-nginx"
ports:
- "5080:80"
- "5443:443"
volumes:
- "../..:/app:consistent"
depends_on:
- "aut_php"
environment:
PS1: "\\u@\\h:\\w\\$$ "
Dockerfile
FROM nginx:1.15.8-alpine
RUN apk add --no-cache bash
RUN rm -rf /var/cache/apk/*
COPY app.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY app_ssl.crt /etc/ssl/certs/app_ssl.crt
COPY app_ssl.key /etc/ssl/private/app_ssl.key
app.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /app/public;
listen 443 default_server ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/app_ssl.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/app_ssl.key;
location / {
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ ^/index\.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_pass aut_php:9000;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
fastcgi_param HTTP_X_REQUEST_ID $request_id;
internal;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
return 404;
}
}
nginx.conf
user nginx;
# 1 worker process per CPU core.
# Check max: $ grep processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
worker_processes 2;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
# Tells worker processes how many people can be served simultaneously.
# worker_process (2) * worker_connections (2048) = 4096
# Check max: $ ulimit -n
worker_connections 2048;
# Connection processing method. The epoll is efficient method used on Linux 2.6+
use epoll;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format json_combined escape=json
'{'
'"time_local":"$time_local",'
'"client_ip":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"remote_addr":"$remote_addr",'
'"remote_user":"$remote_user",'
'"request":"$request",'
'"status": "$status",'
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",'
'"request_time":"$request_time",'
'"http_referrer":"$http_referer",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",'
'"request_id":"$request_id",'
'"request_trace_id":"$http_x_request_trace_id"'
'}';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log json_combined;
# Used to reduce 502 and 504 HTTP errors.
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
# The sendfile allows transfer data from a file descriptor to another directly in kernel.
# Combination of sendfile and tcp_nopush ensures that the packets are full before being sent to the client.
# This reduces network overhead and speeds the way files are sent.
# The tcp_nodelay forces the socket to send the data.
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
# The client connection can stay open on the server up to given seconds.
keepalive_timeout 65;
# Hides Nginx server version in headers.
server_tokens off;
# Disable content-type sniffing on some browsers.
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
# Enables the Cross-site scripting (XSS) filter built into most recent web browsers.
# If user disables it on the browser level, this role re-enables it automatically on serve level.
add_header X-XSS-Protection '1; mode=block';
# Prevent the browser from rendering the page inside a frame/iframe to avoid clickjacking.
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
# Enable HSTS to prevent SSL stripping.
add_header Strict-Transport-Security 'max-age=31536000; includeSubdomains; preload';
# Prevent browser sending the referrer header when navigating from HTTPS to HTTP.
add_header 'Referrer-Policy' 'no-referrer-when-downgrade';
# Sets the maximum size of the types hash tables.
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# Compress files on the fly before transmitting.
# Compressed files are then decompressed by the browsers that support it.
gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
Testler ve Günlükler
HTTP ve HTTPS günlükleri arasında gerçek bir fark yoktur, bu yüzden blogu kısa tutmak için yalnızca HTTP günlükleri ekleyeceğim. Ayrıca, "doğrudan erişim" ve "Gateway erişimi" ile ilgili olan kayıtlara dikkat edin çünkü çok farklı bilgiler taşırlar. Burada bizi ilgilendiren "Gateway erişimi" ile ilgili olan kayıtlar çünkü bunlar prodüksiyon ortamı ile hemen hemen aynı olacaklardır.
Doğrudan erişim
Gateway proxy sunucusundan geçmeden doğrudan uygulama sunucularına erişiyoruz.
$ curl -i "http://localhost:5080" # Authentication
# $ curl -i "http://localhost:5080/other"
# $ curl -i "http://localhost:5080/other?a=1&b=2"
# Application Nginx log
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:07:46:53 +0000","client_ip":"","remote_addr":"172.21.0.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET / HTTP/1.1","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"2246","request_time":"1.708","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"curl/7.38.0","request_id":"0dc58d378520834c41403bfb3f7f8aae","request_trace_id":""}
Gateway erişimi
Burada Gateway proxy sunucusuna erişiyoruz ki bu da prodüksiyon ortamı gibi olacaktır.
$ curl -i "http://localhost:8080/aut/" # Authentication
# $ curl -i "http://localhost:8080/aut/other"
# $ curl -i "http://localhost:8080/aut/other?a=1&b=2"
# Gateway Nginx logs
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:07:54:20 +0000","client_ip":"","remote_addr":"172.17.0.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET /aut/ HTTP/1.1","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"2531","request_time":"0.111","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"curl/7.38.0","request_id":"7a3c97e09964d32de6f6e19871f7c39b"}
# Application Nginx log
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:07:54:20 +0000","client_ip":"172.17.0.1","remote_addr":"172.21.0.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET / HTTP/1.0","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"2519","request_time":"0.107","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"curl/7.38.0","request_id":"28a2ec6d84029f38a19b36771132d666","request_trace_id":"7a3c97e09964d32de6f6e19871f7c39b"}
Docker kurulumum bir Vagrant kutusunda çalışıyor, bu yüzden ana işletim sisteminin tarayıcısından http://192.168.99.30:8080 ile erişerek test ediyorum.
http://192.168.99.30:8080/aut/ # Authentication
# http://192.168.99.30:8080/aut/other
# http://192.168.99.30:8080/aut/other?a=1&b=2
# Gateway Nginx logs
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:07:57:40 +0000","client_ip":"","remote_addr":"192.168.99.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET /aut/ HTTP/1.1","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"1438","request_time":"0.119","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36","request_id":"14291e99a28b964c1bb06435c2cb6b04"}
# Application Nginx log
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:07:57:40 +0000","client_ip":"192.168.99.1","remote_addr":"172.21.0.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET / HTTP/1.0","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"2906","request_time":"0.118","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36","request_id":"286822194b9dcfb8958da91b8a0f7b35","request_trace_id":"14291e99a28b964c1bb06435c2cb6b04"}
Bu örnekte ana makinemi İnternet'e "ngrok" ile açtım, bu yüzden ana işletim sisteminin tarayıcısından http://b119fda7.ngrok.io (192.168.99.30:8080 adresine bağlı) ile erişerek test ediyorum.
http://b229fda7.ngrok.io/aut/ # Authentication
# http://b229fda7.ngrok.io/aut/other
# http://b229fda7.ngrok.io/aut/other?a=1&b=2
# Gateway Nginx logs
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:08:05:28 +0000","client_ip":"31.127.118.116","remote_addr":"192.168.99.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET /aut/ HTTP/1.1","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"1476","request_time":"0.122","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36","request_id":"c83354e6b40bc1ac1959e642bf892562"}
# Application Nginx log
{"time_local":"06/Apr/2019:08:05:28 +0000","client_ip":"31.127.118.116, 192.168.99.1","remote_addr":"172.21.0.1","remote_user":"","request":"GET / HTTP/1.0","status": "200","body_bytes_sent":"2970","request_time":"0.117","http_referrer":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36","request_id":"bce165ceae2ff2b3d58999b834416301","request_trace_id":"c83354e6b40bc1ac1959e642bf892562"}