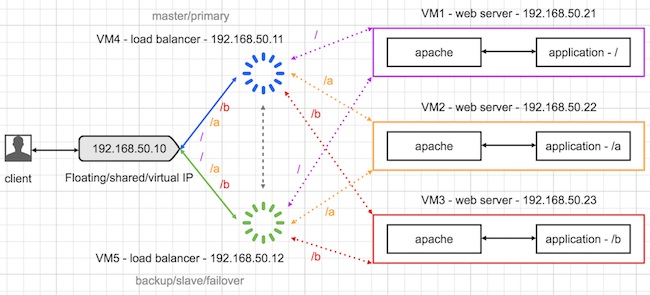
Layer 7 load balancing three different URL based web servers with two different HAProxy servers by providing high-availability with Keepalived in vagrant
15/07/2016 - HAPROXY, VAGRANT
In this example, we're going to send a request to virtual IP, it will be diverted to one of the available Load balancers (HAProxy) then get the response from load balanced three different web servers. Request will be directed to an appropriate web server based on the URL you're trying to consume so it won't be a random process. Request will never go to web servers directly. Load balancer will decide which server to be hit with the request. Example uses vagrant machines and is a layer 7 (application layer) load balancing. Visit here for full configuration manual for you HAProxy version. We also be using Keepalived to make sure that HAProxy servers are up and running and the virtual IP is assigned to running server when one of them is down. It is Keepalived's responsibility.
Three web servers will have only apache running and the load balancer will have HAProxy plus Keepalived running. Load balancer GUI will be accessible from the host machine to see the health and stats about the web servers. Web server 2 will serve URLs: /a, /a/ or /a/..... Web server 3 will serve URLs: /b, /b/ or /b/..... Web server 1 will serve URLs which match any other case such as /, /abc, /hello, /inanzzz/hello so on.
Note
This is a vagrant based example so if the Keepalived floating IP doesn't work as expected, it doesn't mean that it won't work as expected if you do everything manually on the servers so I suggest you to try installing packages manually on a fresh servers.
What we do here
Configuration
I'm assuming that you already have installed vagrant and Oracle VM software. I also assume that the ubuntu/trusty64 box is already added to your filesystem with vagrant box add ubuntu/trusty64 command. If you're not sure, you can confirm it with ls -l ~/.vagrant.d/boxes/ command.
Create a new project folder
mkdir lay7-hap2-web3
$ cd lay7-hap2-web3/
Create webserver.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# BEGIN ########################################################################
echo -e "-- ---------- --\n"
echo -e "-- BEGIN ${HOSTNAME} --\n"
echo -e "-- ---------- --\n"
# VARIABLES ####################################################################
echo -e "-- Setting global variables\n"
APACHE_CONFIG=/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
SITES_ENABLED=/etc/apache2/sites-enabled
LOCALHOST=localhost
# BOX ##########################################################################
echo -e "-- Updating packages list\n"
apt-get update -y -qq
# APACHE #######################################################################
echo -e "-- Installing Apache web server\n"
apt-get install -y apache2 > /dev/null 2>&1
echo -e "-- Adding ServerName to Apache config\n"
grep -q "ServerName ${LOCALHOST}" "${APACHE_CONFIG}" || echo "ServerName ${LOCALHOST}" >> "${APACHE_CONFIG}"
echo -e "-- Updating vhost file\n"
cat > ${SITES_ENABLED}/000-default.conf <<EOF
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
SetEnvIf Request_Method OPTIONS do-not-log-haproxy-ping
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/error.log
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/access.log combined env=!do-not-log-haproxy-ping
</VirtualHost>
EOF
echo -e "-- Adding a custom LogFormat to Apache config catch client's request IP\n"
grep -q 'LogFormat "%{X-Forwarded-For}i %l %u %t \\"%r\\" %>s %b \\"%{Referer}i\\" \\"%{User-Agent}i\\"" combined' ${APACHE_CONFIG} || echo 'LogFormat "%{X-Forwarded-For}i %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined' >> ${APACHE_CONFIG}
echo -e "-- Restarting Apache web server\n"
service apache2 restart
# TEST #########################################################################
echo -e "-- Creating a dummy index.html file\n"
cat > /var/www/html/index.html <<EOD
<html>
<head>
<title>${HOSTNAME}</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${HOSTNAME}</h1>
<p>Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!</p>
</body>
</html>
EOD
# END ##########################################################################
echo -e "-- -------- --"
echo -e "-- END ${HOSTNAME} --"
echo -e "-- -------- --"
Create haproxy.sh
You can create a listen block to listen on a private IP and port for just "stats" configs.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# BEGIN ########################################################################
echo -e "-- ---------- --\n"
echo -e "-- BEGIN ${HOSTNAME} --\n"
echo -e "-- ---------- --\n"
# VARIABLES ####################################################################
echo -e "-- Setting global variables\n"
SYSCTL_CONFIG=/etc/sysctl.conf
# BOX ##########################################################################
echo -e "-- Updating packages list\n"
apt-get update -y -qq
# HAPROXY ######################################################################
echo -e "-- Installing HAProxy\n"
apt-get install -y haproxy > /dev/null 2>&1
echo -e "-- Enabling HAProxy as a start-up deamon\n"
cat > /etc/default/haproxy <<EOF
ENABLED=1
EOF
echo -e "-- Configuring HAProxy\n"
cat > /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg <<EOF
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0
log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
daemon
maxconn 2000
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
retries 3
option redispatch
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
frontend http-in
bind *:80
acl url_a path_reg ^\/a$|\/a\/
use_backend webservers_a if url_a
acl url_b path_reg ^\/b$|\/b\/
use_backend webservers_b if url_b
default_backend webservers_main
backend webservers_main
mode http
stats enable
stats auth admin:admin
stats uri /haproxy?stats
balance roundrobin
option httpchk
option forwardfor
option http-server-close
server web1 192.168.50.21:80 maxconn 32 check
backend webservers_a
mode http
stats enable
stats auth admin:admin
stats uri /haproxy?stats
balance roundrobin
option httpchk
option forwardfor
option http-server-close
server web2 192.168.50.22:80 maxconn 32 check
backend webservers_b
mode http
stats enable
stats auth admin:admin
stats uri /haproxy?stats
balance roundrobin
option httpchk
option forwardfor
option http-server-close
server web3 192.168.50.23:80 maxconn 32 check
EOF
echo -e "-- Validating HAProxy configuration\n"
haproxy -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg -c
echo -e "-- Starting HAProxy\n"
service haproxy start
# KEEPALIVED ###################################################################
echo -e "-- Installing Keepalived\n"
apt-get install -y keepalived > /dev/null 2>&1
echo -e "-- Allowing HAProxy to bind to the virtual IP address\n"
grep -q "net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1" "${SYSCTL_CONFIG}" || echo "net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1" >> "${SYSCTL_CONFIG}"
echo -e "-- Enabling virtual IP binding\n"
sysctl -p
echo -e "-- Configuring Keepalived\n"
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf <<EOF
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy"
interval 2
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
interface eth1 # This may be eth0
state MASTER
virtual_router_id 51
priority ${PRIORITY}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.50.10
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
}
EOF
echo -e "-- Starting Keepalived\n"
service keepalived start
# END ##########################################################################
echo -e "-- -------- --"
echo -e "-- END ${HOSTNAME} --"
echo -e "-- -------- --"
Create Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
# Configs for haproxy 1 (master)
config.vm.define :hap1 do |hap1_config|
hap1_config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb_config|
vb_config.name = "HAProxy 1 - lay7-hap2-web3"
end
hap1_config.vm.hostname = "hap1"
hap1_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.11"
hap1_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "haproxy.sh", env: {"PRIORITY" => "101"}
end
# Configs for haproxy 2 (backup)
config.vm.define :hap2 do |hap2_config|
hap2_config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb_config|
vb_config.name = "HAProxy 2 - lay7-hap2-web3"
end
hap2_config.vm.hostname = "hap2"
hap2_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.12"
hap2_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "haproxy.sh", env: {"PRIORITY" => "100"}
end
# Configs for web server 1
config.vm.define :web1 do |web1_config|
web1_config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb_config|
vb_config.name = "Web Server 1 - lay7-hap2-web3"
end
web1_config.vm.hostname = "web1"
web1_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.21"
web1_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "webserver.sh"
end
# Configs for web server 2
config.vm.define :web2 do |web2_config|
web2_config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb_config|
vb_config.name = "Web Server 2 - lay7-hap2-web3"
end
web2_config.vm.hostname = "web2"
web2_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.22"
web2_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "webserver.sh"
end
# Configs for web server 3
config.vm.define :web3 do |web3_config|
web3_config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb_config|
vb_config.name = "Web Server 3 - lay7-hap2-web3"
end
web3_config.vm.hostname = "web3"
web3_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.23"
web3_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "webserver.sh"
end
end
Run vagrant boxes
$ vagrant up --provision
Bringing machine 'web1' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'web2' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'hap1' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'hap2' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> hap1: -- ---------- --
==> hap1: -- BEGIN hap1 --
==> hap1: -- ---------- --
==> hap1: -- Setting global variables
==> hap1: -- Updating packages list
==> hap1: -- Installing HAProxy
==> hap1: -- Enabling HAProxy as a start-up deamon
==> hap1: -- Configuring HAProxy
==> hap1: -- Validating HAProxy configuration
==> hap1: Configuration file is valid
==> hap1: -- Starting HAProxy
==> hap1: * Starting haproxy haproxy
==> hap1: ...done.
==> hap1: -- Installing Keepalived
==> hap1: -- Allowing HAProxy to bind to the virtual IP address
==> hap1: -- Enabling virtual IP binding
==> hap1: net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
==> hap1: -- Configuring Keepalived
==> hap1: -- Starting Keepalived
==> hap1: * Starting keepalived keepalived
==> hap1: ...done.
==> hap1: -- -------- --
==> hap1: -- END hap1 --
==> hap1: -- -------- --
==> hap2: -- ---------- --
==> hap2: -- BEGIN hap2 --
==> hap2: -- ---------- --
==> hap2: -- Setting global variables
==> hap2: -- Updating packages list
==> hap2: -- Installing HAProxy
==> hap2: -- Enabling HAProxy as a start-up deamon
==> hap2: -- Configuring HAProxy
==> hap2: -- Validating HAProxy configuration
==> hap2: Configuration file is valid
==> hap2: -- Starting HAProxy
==> hap2: * Starting haproxy haproxy
==> hap2: ...done.
==> hap2: -- Installing Keepalived
==> hap2: -- Allowing HAProxy to bind to the virtual IP address
==> hap2: -- Enabling virtual IP binding
==> hap2: net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
==> hap2: -- Configuring Keepalived
==> hap2: -- Starting Keepalived
==> hap2: * Starting keepalived keepalived
==> hap2: ...done.
==> hap2: -- -------- --
==> hap2: -- END hap2 --
==> hap2: -- -------- --
==> web1: -- ---------- --
==> web1: -- BEGIN web1 --
==> web1: -- ---------- --
==> web1: -- Setting global variables
==> web1: -- Updating packages list
==> web1: -- Installing Apache web server
==> web1: -- Adding ServerName to Apache config
==> web1: -- Updating vhost file
==> web1: -- Adding a custom LogFormat to Apache config catch client's request IP
==> web1: -- Restarting Apache web server
==> web1: * Restarting web server apache2
==> web1: ...done.
==> web1: -- Creating a dummy index.html file
==> web1: -- -------- --
==> web1: -- END web1 --
==> web1: -- -------- --
==> web2: -- ---------- --
==> web2: -- BEGIN web2 --
==> web2: -- ---------- --
==> web2: -- Setting global variables
==> web2: -- Updating packages list
==> web2: -- Installing Apache web server
==> web2: -- Adding ServerName to Apache config
==> web2: -- Updating vhost file
==> web2: -- Adding a custom LogFormat to Apache config catch client's request IP
==> web2: -- Restarting Apache web server
==> web2: * Restarting web server apache2
==> web2: ...done.
==> web2: -- Creating a dummy index.html file
==> web2: -- -------- --
==> web2: -- END web2 --
==> web2: -- -------- --
==> web3: -- ---------- --
==> web3: -- BEGIN web3 --
==> web3: -- ---------- --
==> web3: -- Setting global variables
==> web3: -- Updating packages list
==> web3: -- Installing Apache web server
==> web3: -- Adding ServerName to Apache config
==> web3: -- Updating vhost file
==> web3: -- Adding a custom LogFormat to Apache config catch client's request IP
==> web3: -- Restarting Apache web server
==> web3: * Restarting web server apache2
==> web3: ...done.
==> web3: -- Creating a dummy index.html file
==> web3: -- -------- --
==> web3: -- END web3 --
==> web3: -- -------- --
Access the machines
# Server 1
$ vagrant ssh web1
vagrant@web1:~$
# Server 2
$ vagrant ssh web2
vagrant@web2:~$
# Server 3
$ vagrant ssh web3
vagrant@web3:~$
# HAProxy 1
$ vagrant ssh hap1
vagrant@hap1:~$
# HAProxy 2
$ vagrant ssh hap2
vagrant@hap2:~$
Verifying Keepalived Virtual IP
As you can see below, the virtual IP has been assigned to hap1 which is master. Just pay attention to inet 192.168.50.10/32 scope global eth1. As you can see, it doesn't appear in hap2 because it is backup.
HAProxy 1
vagrant@hap1:~$ sudo ip addr sh eth1
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:79:c5:df brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.50.11/24 brd 192.168.50.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.50.10/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe79:c5df/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
HAProxy 2
vagrant@hap2:~$ sudo ip addr sh eth1
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:17:29:f3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.50.12/24 brd 192.168.50.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe17:29f3/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
If you stop HAProxy server on hap1, Keepalived will assign virtual IP to hap2 so as a result inet 192.168.50.10/32 scope global eth1 will appear in hap2 because it is master now. If you use sudo cat /var/log/syslog on both servers, you'll see master and backup state changes.
Tests
In normal life web servers must not be directly accessible but I ignore it for now for testing purposes. HAProxy servers are not accessible directly but the virtual IP we created with Keepalived will be used instead which is how it should be.
Web server 1
Response to request below will alway be the same.
# Request
http://192.168.50.21/
# Response
web1
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
Web server 2
Response to request below will alway be the same.
# Request
http://192.168.50.22/
# Response
web2
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
Web server 3
Response to request below will alway be the same.
# Request
http://192.168.50.23/
# Response
web3
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
Load balancer
Response will always change because request is evenly shared between web servers. Load balancer does it!
# Request
http://192.168.50.10/
# Response
web1
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
# Request
http://192.168.50.10/
# Response
web2
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
# Request
http://192.168.50.10/
# Response
web3
Hi sir, I am going to serve you today!
System outage tests
Web servers
If you bring any of web servers, corresponding system will go down because they all have only one server instances so you will see error below.
503 Service Unavailable
No server is available to handle this request.
Bring only haproxy 1 down
Keepalived will assign virtual IP to hap2 and traffic will be handled by it so system will still be up and running.
Bring only haproxy 2 down
Keepalived will assign virtual IP to hap1 and traffic will be handled by it so system will still be up and running.
Bring both haproxy 1 and 2 down
System will go down because we only have two load balancer servers.
Session handling
In web applications, user sessions are stored in temporary area in the server. If you're using load balancer, as we know user will be bounced to different server per request. In such cases, application won't be able to get session information of user from the current server and potentially he'll be logged out from the application so on. There are three options to solve this issue:
- Cookie-based Sessions: Session data is stored in browser's cookie. It has limitations such as amount of data a cookie can store. Also it exposes security issues such as it can be hijacked.
- Sticky Sessions/Session Affinity: This will ensure that given user will always be routed to same server for his subsequent requests. Web server saves session locally. The problem is sharing of work load between web servers is not really load balanced anymore but still better than the first option.
- Central Session Storage: Storing session data in Redis, memcached, database etc. Web servers will always connect to same storage so user session will always be available on which ever server user is routed to. This is the best solution.
Webserver logs
General
Keepalived pings HAProxy every 2 seconds then the request logs get added to Apache access.log file by default. This bloats the access.log file so to prevent recording such request logs, we modified /etc/apache2/sites-enabled as shown below.
SetEnvIf Request_Method OPTIONS do-not-log-haproxy-ping
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/access.log combined env=!do-not-log-haproxy-ping
If a client sends a request to load balancer via http://192.168.50.10, request gets directed to one of the available web servers and the request is logged in access.log file as follows.
192.168.50.11 - - [09/Jul/2016:13:22:52 +0000] "OPTIONS / HTTP/1.0" 200 180 "-" "-"
192.168.50.12 - - [09/Jul/2016:13:22:53 +0000] "OPTIONS / HTTP/1.0" 200 180 "-" "-"
192.168.50.11 - - [09/Jul/2016:13:22:54 +0000] "OPTIONS / HTTP/1.0" 200 180 "-" "-"
192.168.50.12 - - [09/Jul/2016:13:22:55 +0000] "OPTIONS / HTTP/1.0" 200 180 "-" "-"
As you can see above, only HAProxy IP's are get recorded which can be useless in real life scenario. To get client's data, we added line below to /etc/apache2/apache2.conf.
LogFormat "%{X-Forwarded-For}i %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
Now the request is logged in access.log file as follows.
192.168.50.1 - - [09/Jul/2016:13:24:24 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 117 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [09/Jul/2016:14:42:44 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 117 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.10; rv:47.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/47.0"
You can use sudo tail -f /var/log/apache2/access.log on each web server to see activities in real-time.
Web server specific
Web server 1 will show logs below when you call: http://192.168.50.10/, http://192.168.50.10/aaa and http://192.168.50.10/bbb
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:32:41 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 112 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:33:13 +0000] "GET /aaa HTTP/1.1" 404 279 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:33:37 +0000] "GET /bbb HTTP/1.1" 404 279 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
Web server 2 will show logs below when you call: http://192.168.50.10/a, http://192.168.50.10/a/ and http://192.168.50.10/a/inanzzz
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:32:48 +0000] "GET /a HTTP/1.1" 404 277 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:32:51 +0000] "GET /a/ HTTP/1.1" 404 278 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:32:58 +0000] "GET /a/inanzzz HTTP/1.1" 404 285 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
Web server 3 will show logs below when you call: http://192.168.50.10/b, http://192.168.50.10/b/ and http://192.168.50.10/b/inanzzz
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:33:26 +0000] "GET /b HTTP/1.1" 404 277 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:33:29 +0000] "GET /b/ HTTP/1.1" 404 278 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
192.168.50.1 - - [15/Jul/2016:14:33:34 +0000] "GET /b/inanzzz HTTP/1.1" 404 285 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36"
HAProxy Iogs
After stopping and starting HAProxy services on both servers, you'll see state logs like below.
# hap1
Jul 14 20:51:52 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Script(chk_haproxy) succeeded
Jul 14 20:51:53 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Transition to MASTER STATE
Jul 14 20:51:54 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Entering MASTER STATE
Jul 14 20:53:06 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Received lower prio advert, forcing new election
Jul 14 21:01:36 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Script(chk_haproxy) failed
Jul 14 21:01:38 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Received higher prio advert
Jul 14 21:01:38 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[3026]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Entering BACKUP STATE
# hap2
Jul 14 20:53:05 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Script(chk_haproxy) succeeded
Jul 14 20:53:06 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Transition to MASTER STATE
Jul 14 20:53:06 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Received higher prio advert
Jul 14 20:53:06 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Entering BACKUP STATE
Jul 14 21:00:38 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Script(chk_haproxy) failed
Jul 14 21:01:18 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Script(chk_haproxy) succeeded
Jul 14 21:01:38 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) forcing a new MASTER election
Jul 14 21:01:39 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Transition to MASTER STATE
Jul 14 21:01:40 vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64 Keepalived_vrrp[2973]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) Entering MASTER STATE
HAProxy stats GUI
Load balancer stats are served via http://192.168.50.10/haproxy?stats and the credentials as admin:admin. Information, will also come from the master/primary load balancer unless it is down. If it is down, backup/slave/failover load balancer will serve the stats. You can run $ ps aux | grep haproxy command on each servers and compare resulting PID to what you see in web interface where it says "Statistics Report for pid 8038".
Visit http://192.168.50.30/haproxy?stats. Login with admin:admin.
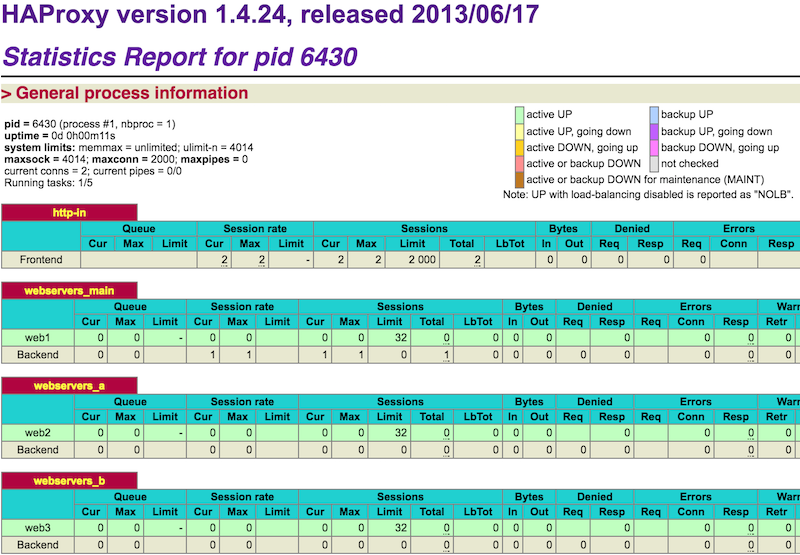
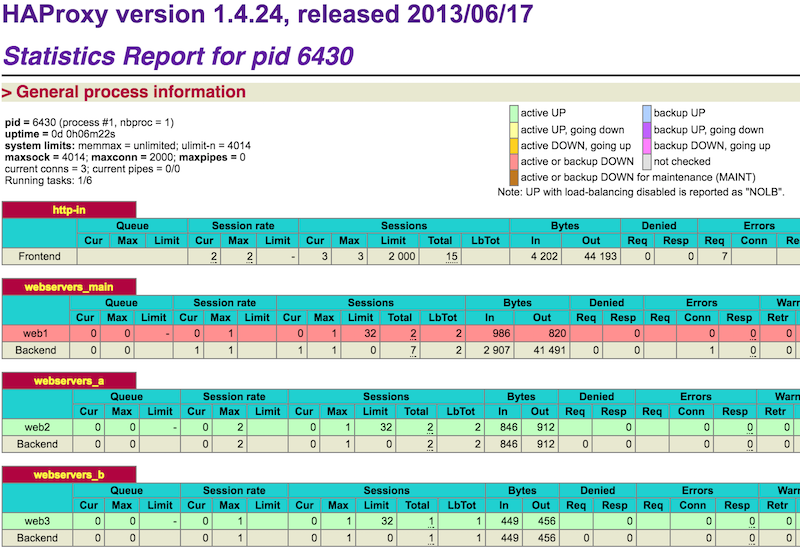
Readings
- An Introduction to HAProxy and Load Balancing Concepts
- Load balancing, affinity, persistence, sticky sessions: What you need to know
- So You Got Yourself a Loadbalancer
- Load Balancing with HAProxy